Apache Kafka is a popular distributed streaming platform used for building realtime data pipelines and streaming apps.
Getting started
RudderStack supports sending events to Apache Kafka via the following connection modes:
| Connection Mode | Web | Mobile | Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device mode | - | - | - |
| Cloud mode | Supported | Supported | Supported |
Once you have confirmed that the source platform supports sending events to Apache Kafka, follow these steps:
- From your RudderStack dashboard, add the source. Then, from the list of destinations, select Apache Kafka.
- Assign a name to your destination and click Continue.
Connection settings
To successfully set up Apache Kafka as a destination, you need to configure the following settings:
- Host Name(s): Enter your Kafka server broker's host name. You can specify multiple host names in a comma-separated format.
- Port: Enter the port number to connect to the Kafka broker.
- Topic Name: Specify the default Kafka topic where you want to send the event data.
- SSL Enabled: Enable this option if you have enabled SSL to connect to your broker.
- CA Certificate: If SSL is enabled, enter the CA certificate.
- Enable SASL with SSL: Enable this setting to use SASL for client authentication.
- SASL Type: Choose the SASL authentication type from Plain, SCRAM SHA-512, and SCRAM SHA-256.
- Username: Enter the username configured in Kafka for authenticating clients with SASL.
- Password: Enter the password for the above username.
- Convert Data to AVRO format: Enable this setting to serialize your data using Avro and send it to the specified Kafka topic.
- Schema ID: Enter the schema ID for the schema list.
- Schema: Enter the schema corresponding to the above-mentioned ID.
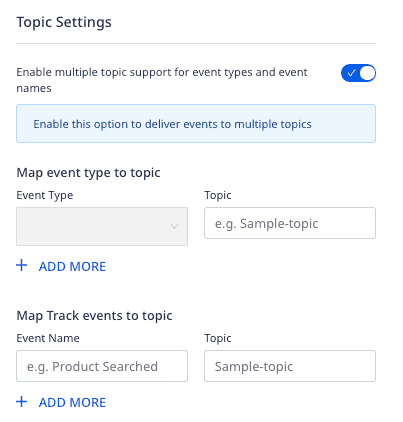
- Enable multiple topic support for event types and event names: Enable this setting to deliver your events to multiple Kafka topics.
track events with the above setting, RudderStack sends the rest of the events to the topic defined in the Topic Name setting.Sending events to Kafka topics
You can send your events to a specific Kafka topic by configuring the Topic Name dashboard setting.
Alternatively, you can send your events to a Kafka topic by specifying the topic name in the integrations object, as shown:
rudderanalytics.track( "Feedback Submitted", { feedbackScore: 9, feedbackText: "Great Product!", ip: "127.0.0.0", url: "https://www.google.com/", createdAt: "2022-01-20T13:39:21.032Z" }, { integrations: { "All": true, "Kafka": { "topic": "myTopic", }, }, });integrations object take precedence over the dashboard settings.RudderStack also supports sending events to multiple Kafka topics. To do so, enable the Enable multiple topic support for event types and event names dashboard setting and configure the mappings, as shown:
Serializing data using Avro
RudderStack lets you serialize your data using Avro and send it to a specific Kafka topic by leveraging the goavro package.
To use this feature, you need to pass the schemaId in your event's integrations object, as shown in the below event payload:
{ "event": "Product Added", "messageId": "4bb69e26-b5a6-446a-a140-dbb6263369c9", "type": "track", "anonymousId": "", "context": { "traits": { "email": "alex@example.com" }, }, "integrations": { "KAFKA": { "schemaId": "schema001" } }, "originalTimestamp": "2022-06-22T12:31:19.002+05:30", "receivedAt": "2022-06-22T12:31:15.656+05:30", "request_ip": "[::1]", "sentAt": "2022-06-22T12:31:19.002+05:30", "timestamp": "2022-06-22T12:31:15.655+05:30"}The corresponding schema is shown below:
{"name":"RudderStackEvent","type":"record","namespace":"com.acme.avro","fields":[{"name":"anonymousId","type":"string"},{"name":"event","type":"string"},{"name":"messageId","type":"string"},{"name":"originalTimestamp","type":"string"},{"name":"receivedAt","type":"string"},{"name":"request_ip","type":"string"},{"name":"rudderId","type":"string"},{"name":"sentAt","type":"string"},{"name":"timestamp","type":"string"},{"name":"type","type":"string"},{"name":"context","type":"record","fields":[{"name":"traits","type":"record","fields":[{"name":"email","type":"string"}]},{"name":"ip","type":"string"}]},{"name":"integrations","type":"record","fields":[{"name":"KAFKA","type":"record","fields":[{"name":"schemaId","type":"string"}]}]}]}Partition key
RudderStack uses the userId in the event as the partition key of the message.
userId is not present in payload, then RudderStack uses anonymousId instead.So, if you have a multi-partitioned topic, then the records of the same userId (or anonymousId in absence of userId) will always go to the same partition.
FAQ
Does my Kafka server require client authentication?
If you have enabled 2-way SSL, that is, your server requires client authentication, then you need to have the CA certificate and put that in the truststore of your server.
How can I enable the 2-way SSL in Kafka and connect to RudderStack?
Follow the below steps to make use of Java's keytool utility to enable two-way SSL in Kafka and connect to RudderStack:
Step 1: Generate the key and certificate
Run the following command:
keytool -keystore kafka.server.keystore.jks -alias localhost -keyalg RSA -genkeyStep 2: Create your own CA
Follow these steps to create your own CA:
- Generate a CA that is a public-private key pair and a certificate by running the command below. Enter the contents of this certificate in the RudderStack dashboard under the CA certificate setting.
openssl req -new -x509 -keyout ca-key -out ca-cert -days {validity}Add the generated CA to the broker's truststore so that the brokers can trust this CA.
keytool -keystore kafka.server.truststore.jks -alias CARoot -importcert -file ca-cert
Step 3: Sign the certificate
Follow the steps below:
- Export the certificate from the keystore, as shown:
keytool -keystore kafka.server.keystore.jks -alias localhost -certreq -file cert-file- Sign it with the CA, as shown:
openssl x509 -req -CA ca-cert -CAkey ca-key -in cert-file -out cert-signed -days {validity} -CAcreateserial -passin pass:{ca-password}- Import both the certificate of the CA and the signed certificate into the broker keystore, as shown:
keytool -keystore kafka.server.keystore.jks -alias CARoot -import -file ca-certkeytool -keystore kafka.server.keystore.jks -alias localhost -import -file cert-signedAll the above commands to generate the key and certificate, create the CA, and sign the certificate are summarized below:
// Step 1: Generate the key and the certificatekeytool -keystore kafka.server.keystore.jks -alias localhost -keyalg RSA -validity {validity} -genkey// Step 2: Create your own CAopenssl req -new -x509 -keyout ca-key -out ca-cert -days {validity}keytool -keystore kafka.server.truststore.jks -alias CARoot -importcert -file ca-cert// Step 3: Sign the certificatekeytool -keystore kafka.server.keystore.jks -alias localhost -certreq -file cert-fileopenssl x509 -req -CA ca-cert -CAkey ca-key -in cert-file -out cert-signed -days {validity} -CAcreateserial -passin pass:{ca-password}keytool -keystore kafka.server.keystore.jks -alias CARoot -import -file ca-certkeytool -keystore kafka.server.keystore.jks -alias localhost -import -file cert-signedStep 4: Update server.properties
Enter the below parameters in your server.properties:
ssl.keystore.location=<keystore location>ssl.keystore.password=<keystore password>ssl.key.password=<ca key password>ssl.truststore.location=<truststore location>ssl.truststore.password=<truststore password>ssl.client.auth=requiredssl.enabled.protocols=TLSv1.2,TLSv1.1,TLSv1ssl.truststore.type=JKSssl.keystore.type=JKSStep 5: Save the RudderStack certificate
Save the below RudderStack certificate as ca-cert-rudder (or any other name of your choice) on your system:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----MIIEDzCCAvegAwIBAgIUByH8aYuRqjCyz5yZZ91fcJOsW+0wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQAwgZYxCzAJBgNVBAYTAklOMRQwEgYDVQQIDAtXZXN0IEJlbmdhbDEQMA4GA1UEBwwHS29sa2F0YTEUMBIGA1UECgwLUnVkZGVyc3RhY2sxCzAJBgNVBAsMAklUMRQwEgYDVQQDDAtSdWRkZXJzdGFjazEmMCQGCSqGSIb3DQEJARYXY29udGFjdEBydWRkZXJzdGFjay5jb20wHhcNMjAwNTE5MTA1OTEwWhcNMjEwNTE5MTA1OTEwWjCBljELMAkGA1UEBhMCSU4xFDASBgNVBAgMC1dlc3QgQmVuZ2FsMRAwDgYDVQQHDAdLb2xrYXRhMRQwEgYDVQQKDAtSdWRkZXJzdGFjazELMAkGA1UECwwCSVQxFDASBgNVBAMMC1J1ZGRlcnN0YWNrMSYwJAYJKoZIhvcNAQkBFhdjb250YWN0QHJ1ZGRlcnN0YWNrLmNvbTCCASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBAMkLBYbfhvhm2wpJFZSr9AGyrJUEh2e6YaY83xLRDuOYC1cvqlmCNxltc4W+ACyyi9zqSvhrrNb2C/YhIg4gvvplImAAmv5Ua4ZiB2XSrn9ZvR+baRyezPgKI1+iU5ovDciUkeZP3p7hEmLwktayyFrWV5IEuGnfGBN4O077tgUiCm8zq3cHC0e5JBTUtelnwj6u1Ye6zZfIx/rCIkf0l1LGZqV1DHZefCqPl3l9awVnA4rbllL9a+mLNe44BT2H4UG6OaZxnAEqVQ9xlMvvDAYSzaSI334qGw/AAeBUE3mHyEbE9PtS0p+qOdRiq4b5m+usW5VbZBFSvT4AFR2Xa2cCAwEAAaNTMFEwHQYDVR0OBBYEFF71gmg4bAdft9PF3Sj9QMrxwoFMMB8GA1UdIwQYMBaAFF71gmg4bAdft9PF3Sj9QMrxwoFMMA8GA1UdEwEB/wQFMAMBAf8wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQADggEBAFvXp77ZQXwqB0vQZXAr4JfiNZueNP4OlpxltiLdqt0UwLJzCZ/ik65jmGGcoxZeFQc3dF8InheH+zvanPWBq385TDSyF9/vomKbu7+Rb7ndgDtWGpJm6vCUgC6m15KRKzjlHmiWu227hed4ZNrl5EJwqqFhKzSQ62wv66uMxHaTVaC1ThV5MmecsC7kS3mNCkhO1IVxy5KAJCftYzjni+O0U0wkcmUnZjJyN0l9hAegB6VLwodW3FqFJ7hMlSZOxE9hYjl9/FlqDdS3KPtn8qh9uliq9V8NELK2jROhvWJxTpadFmHwCTtKNrfnm2PgokxX3pVtkFu7xQhl26+87RQ=-----END CERTIFICATE-----Step 6: Add the RudderStack CA certificate to your truststore
Add the above RudderStack CA certificate to your truststore by using the certificate's location in the following command:
keytool -keystore kafka.server.truststore.jks -alias CARootRudder -import -file ca-cert-rudder// here ca-cert-rudder is the RudderStack CA certificateHow can I connect to RudderStack if my Kafka server is running in a Kubernetes cluster?
You will need to expose one public address to which RudderStack can connect. It is recommended to use SSL for that.
If you use PLAINTEXT for your internal services within your cluster, you might already have the address. Open this address with SSL. You need to update advertised.listeners in your server.properties, as shown in the below example:
# Hostname and port the broker will advertise to producers and consumers.# here the INTERNAL listener is your cluster kafka service host for kafka server# and the EXTERNAL listener is the public loadbalancer for kafka serveradvertised.listeners=INTERNAL://kafka-0.kafka-headless.kafka-test-1.svc.cluster.local:9092,EXTERNAL://ab7e36e84991c11ea8a930ebf847c1ef-555780507.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com:19092listener.security.protocol.map=INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,EXTERNAL:SSLDoes RudderStack support SASL_PLAINTEXT authentication?
RudderStack does not support SASL_PLAINTEXT authentication. You can use SASL_SSL instead. The official Kafka documentation recommends using SASL with SSL in production.
Why is the connection between Kafka and Zookeeper is failing for SASL?
You can try configuring your Zookeeper with SASL_SSL to resolve this issue.
Contact us
For more information on the topics covered on this page, email us or start a conversation in our Slack community.